Activation Functions and their purpose: Binary, Linear, ReLU, Sigmoid, Tanh and Softmax
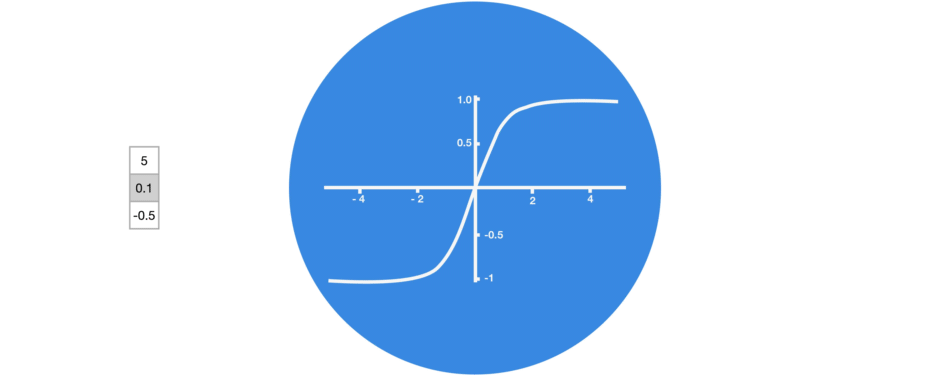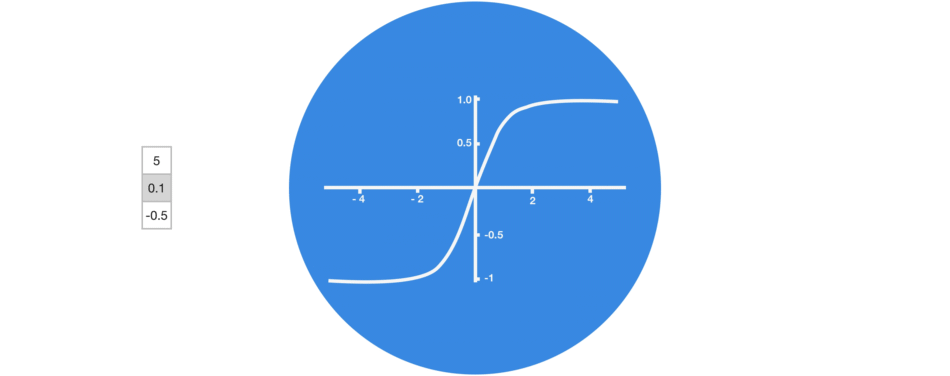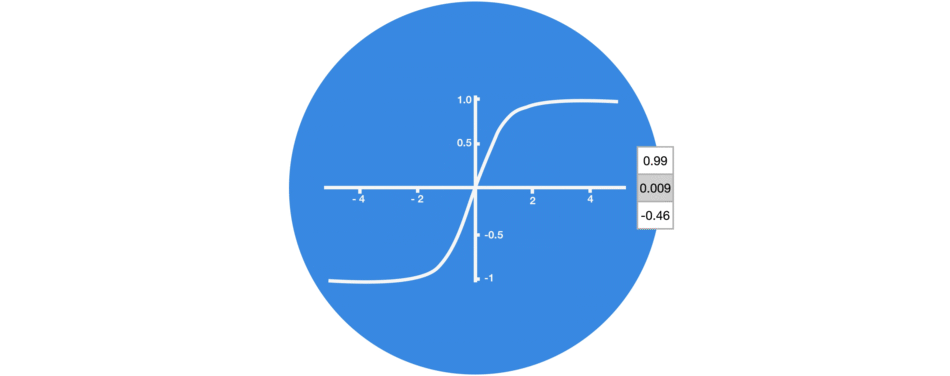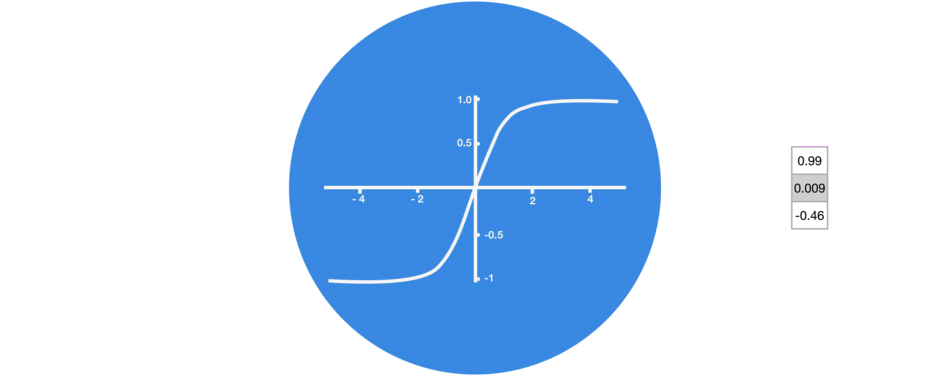
Graphic showing activation function.
What is an activation function?
In the context of a neural network an activation function defines the output of a node/neuron, they could be classified into these categories: Ridge activation functions, Radial activation functions and Folding activation functions.
For this article we will be looking at Ridge activation functions.
1. Binary Step Function
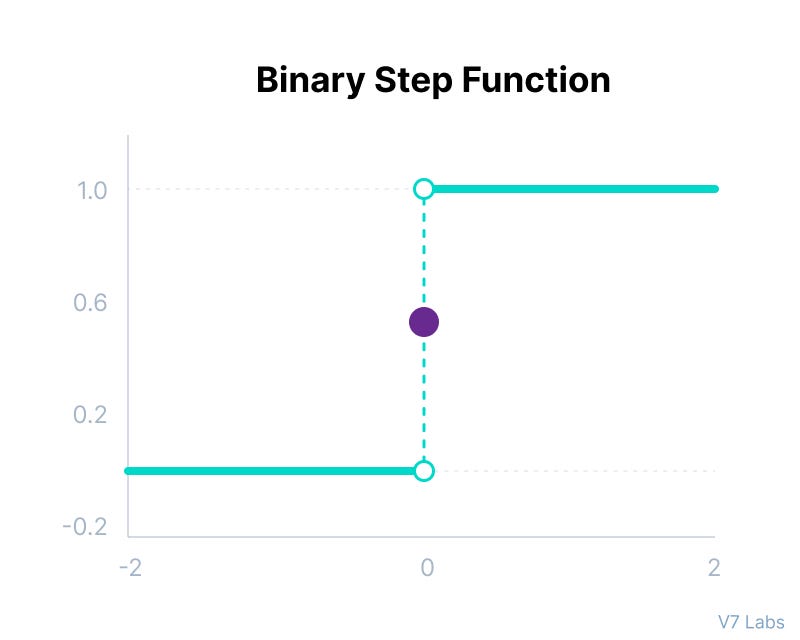
Binary step function is a threshold based activation function meaning that if the input crosses a certain value the neuron is activated and if it goes below that value the neuron is deactivated, this function can be used in tasks of binary classification, This activation function is not suitable at all in the case of non-linearity (most of problem domains). Also, since the network is not differentiable, gradient-based training is not possible.
2. Linear activation Function
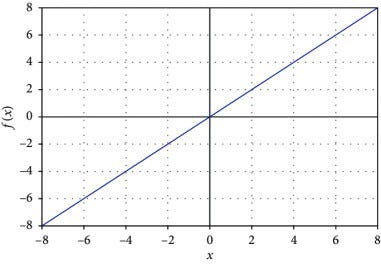
As you can see here our function is directly proportional to the weighted sum of neurons: f(x) = x. With linear activation the changes made in back-propagation will be constant (as the derivative of this function is 1) which is not good for learning, it also goes by the name Identity.
2. Sigmoid
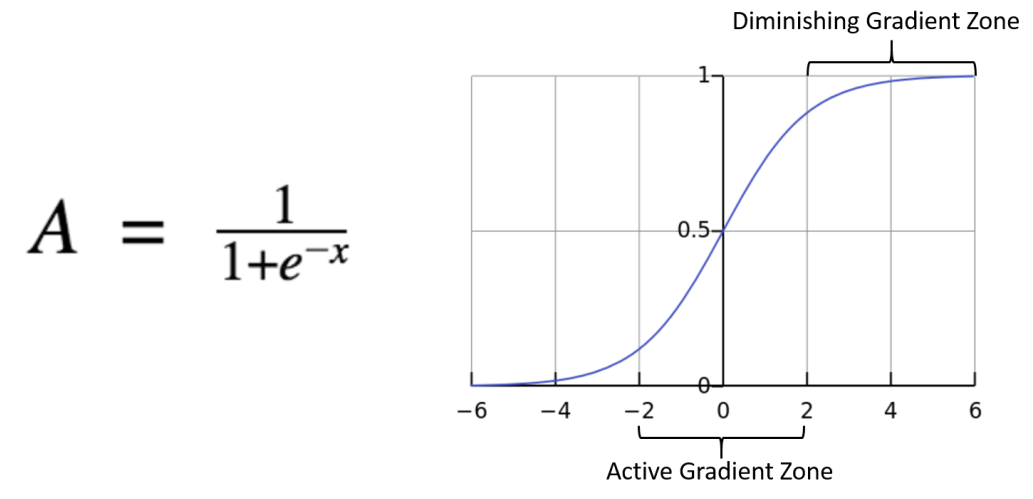
The sigmoid function also known as the logistic function and it’s the one used in logistic regression, it takes a probabilistic approach and the output ranges between from 0 and 1, it essentially normalizes the output those values, However like in the graphic above the sigmoid function makes almost no change in prediction for very high or very low inputs, this problem is known as the vanishing gradient.
2. 1. Softmax
The Softmax function is a generalization of the sigmoid function for multiple classes it’s typically used in the output for normalizes the output of the previous unit and turns it into a range of probabilities of each class.
3. Tanh
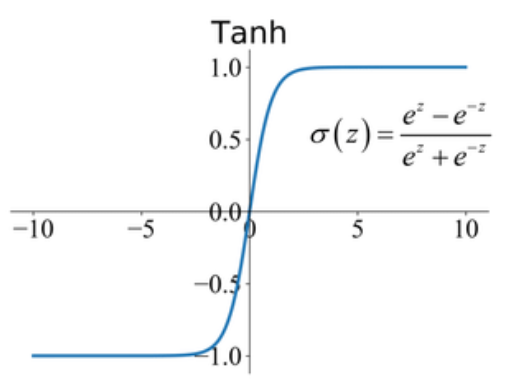
tanh function (also known as hyperbolic tangent) is almost like the sigmoid function but slightly better than that since it’s output ranges between -1 and 1 allowing negative outputs. However, tanh also comes with the vanishing gradient problem just like sigmoid function.
4. ReLU (Rectified Linear Unit)
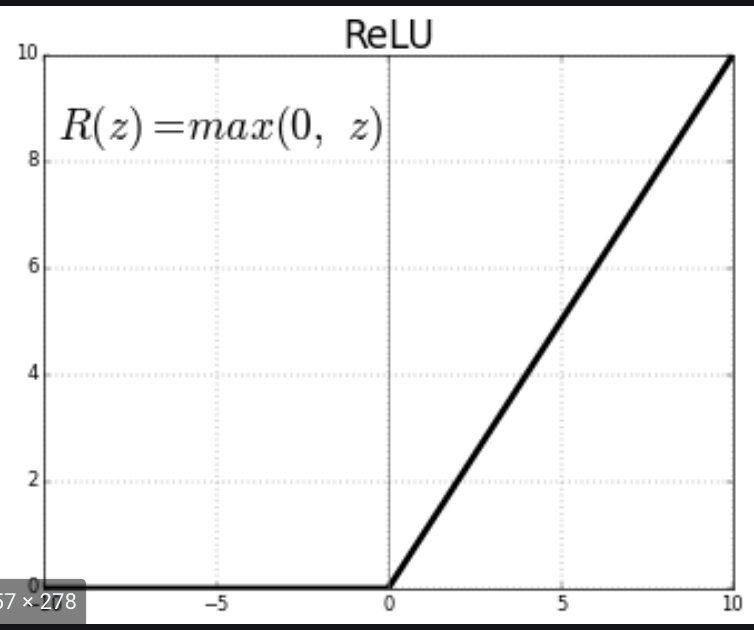
ReLU is a simple calculation that returns the value provided as input directly, or the value 0.0 if the input is 0.0 or less. basically it can be described into an if statement. To quote Ian Goodfellow in his deep learning book
“Because rectified linear units are nearly linear, they preserve many of the properties that make linear models easy to optimize with gradient-based methods. They also preserve many of the properties that make linear models generalize well.
Basically ReLU manages to circumvent the vanishing gradient problem in the sigmoid and tanh functions.
Conclusion
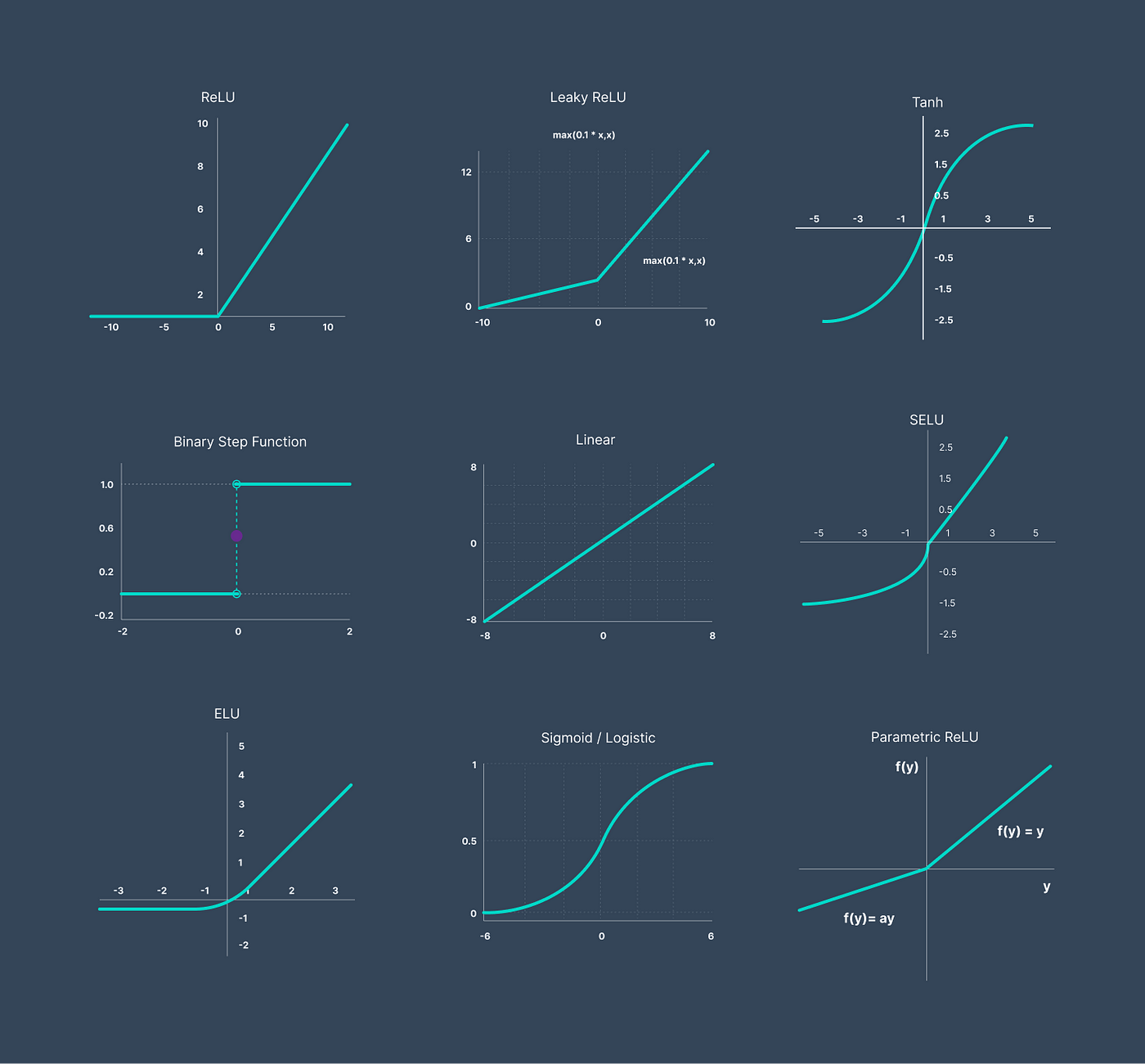
In this article we discussed different activation functions, but as a matter of fact more functions exist especially variants of these like leakyReLU which takes in negative values and normalizes them, Next time we will be discovering the different Optimization techniques.